Money Laundering Statistics By Crime Category, Country And Facts (2025)

Updated · Jun 23, 2025


WHAT WE HAVE ON THIS PAGE
Introduction
Money Laundering Statistics: Indeed, money laundering remains a big social problem across most economies and their financial systems. Most criminals aim to conceal the illicit sources of their funds and present them as clean. It is in the year 2024 when the extent of money laundering is at a crisis level in several nations.
This piece will contain relevant money laundering statistics on a global scale in 2024, including the effects, financial repercussions, and politics surrounding the existing policies to curb the vice.
Editor’s Choice
- Money laundering statistics reveal that the annual fraud volume in the United States alone exceeds 300 billion dollars.
- It is estimated that criminals launder between 800 billion and 2 trillion dollars every year in the world.
- In 2022, banks around the world paid 10.4 billion dollars in fines for failing to prevent money laundering.
- As of 2023, anti-money laundering (AML) software sales were forecasted to be worth 1.77 billion dollars.
- Money laundering has also been characterized by the phenomenon of identity theft.
- Outrageously, the very best among AML initiatives manages only 0.1% return of laundered money. With every year that passes, money laundering is estimated to cost between 2 and 5% of a nation’s GDP.
- The process of money laundering is classically divided into three stages, and organizations such as Standard Chartered Bank have come under fire for failing to adhere to such requirements on a number of occasions.
- It is forecasted that every year on a global scale, between 800 billion and 2 trillion US dollars will still be laundered from the economic system by the year 2024, accounting for about 2% – 5% of the G.D.P. M. worldwide.
- Money laundering statistics indicate that, for instance, in the U.S., approximately US$ 300 million is expected to be lost to money laundering in 2024, which has increased by 15% from the previous period.
- Most peripheral countries in the European Union reported a similar amount, almost 200 billion dollars, to be lost, therefore establishing the region as a money laundering center.
- The financial system continues to be at greater risk, with statistics showing that banks and other financial institutions are involved in 70% of the reported cases of money laundering.
- Money laundering statistics show that the criminal use of virtual coins is increasing at a record pace, with forecasts indicating that in 2024, $23 billion worth of cryptocurrencies will be laundered, which is a 30% increase compared to 2023.
- The purchase of property in a foreign country continues to be a favorite strategy to wash illicit funds, with transactions estimated to be around 60 billion in real estate activities worldwide, zealously pursued in 2024.
- As per the geographical statistics, North America generated nearly 35% of the money laundering activities across the globe in the year 2024, the USA being the most affected country.
- Of the global laundering activities, Europe accounted for 25%, rising from the activities in Eastern Europe and offshore centers.
- Laundering activities in the Asia-Pacific region also increased significantly to 22% of the total world launders, mainly due to increasing cryptocurrency activities in countries like China and India.
- In the year 2024, authorities all over the world were able to confiscate more than one hundred and fifty billion dollars in illegal money, which was an improvement from the one hundred and twenty billion dollars taken out in the year 2023.
- In addition to the combined efforts of nations against money laundering, arrests of the crime went up globally by 20%, with more than 1,125 prosecuted in the United States of America.
Money Laundering Key Facts
- As a practice that takes place clandestinely, it is difficult to ascertain money laundering and its dynamics from a global perspective.
- Money laundering statistics by the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) state that Transnational Organized Crime (TOC) would cost countries somewhere between 2 to 5% of the world’s annual GDP, which translates into billions and trillions of dollars.
- This is because collateral activities that include but are not limited to drug trade, organized crime, scamming, kleptocracy, human trafficking, and funding for terrorism are very much associated with this vice.
- People involved in these crimes make considerable amounts of money. Then, they try to hide that money behind a fake business or integrate it into real financial systems through numerous money laundering or infiltration operations.
- Money laundering occurs all over the world, but the extent and techniques used differ from region to region.
- The countries with the highest money laundering prevalence rates tend to have ineffective controls, high corruption, or poor political administration.
- Countries in Asia, South America, and Africa have also been marked as extremely vulnerable to these vices. Increased prevention of financial crime costs has been noted since the year 2022.
- From 2021 to 2025, a compound annual growth rate of 14% is anticipated in the anti-money laundering software industry.
- As of now, Richmond, Virginia, has recorded the highest incidence of white collar crimes in the US cities, gasping 7504 within 10,000 inhabitants.
- Money laundering statistics indicate that 90% or above of money laundering distressed crimes are said to be self-reported, but 91.1% of those found guilty are jailed.
- Money laundering in the United States is estimated to account for between 15% – 38% of the illicit foreign transfer of funds.
- Partly due to its intermediary nature regarding financial transactions, the banking industry constitutes the sector that is most at risk of money laundering activities.
- There are several other institutions, such as banks, investment and money services businesses, and virtual currencies, which may also act as channels for the laundering of money.
- These days, the attention has moved to digital and cryptocurrency, even more so to prevent the abuse of these systems.
- Those are the few things Governments and international institutions have resolved to do. Anti-money laundering financial policies have been introduced, and financial intelligence units (FIUs), international associations, and anti-money laundering regulations have been established.
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is a very important intergovernmental organization in the implementation of global standards and policies on the enforcement of AML.
- Money laundering statistics, in addition to being a crime, have many social and economic impacts. It interferes with the integrity of markets, promotes corruption, and decreases the populace’s confidence in the banking sector.
- Oftentimes, dirty money ends up funding more illicit activities, thus causing an aggravating loop in different economies.
- The methods of laundering money abstracted from the financial system, for example, in the system of financial crimes, are increasingly sophisticated, which poses another problem for the authorities.
- With the advancement of technology, especially in the forms of virtual currency, internet-based services, and methods of concealing identity, a new dimension of problems has emerged for supervision and enforcement.
- Hence, they need to be creative and proactive in managing these concerns.
Money Laundering Services Used by Crime Category
 (Source: chainalysis.com)
(Source: chainalysis.com)
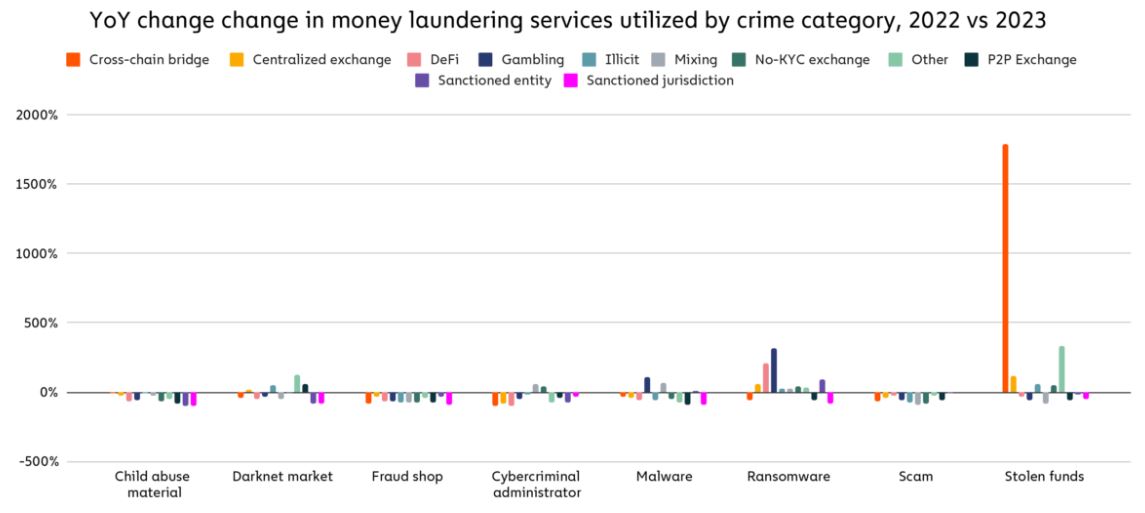
- According to money laundering statistics, if we begin to examine more deeply how different types of crypto criminals launder money, one will be able to note shifts in some aspects in particular.
- The most important of them is the rise in the amount of funds diverted to the cross-chain bridges from wallets associated with hacked funds, which we will elaborate on later.
- Also, an increasing number of funds connected to ransomware addresses are sent to betting sites and from ransomware wallets to cross-chain bridging.
Money Laundering In Mexico
(Reference: statista.com)
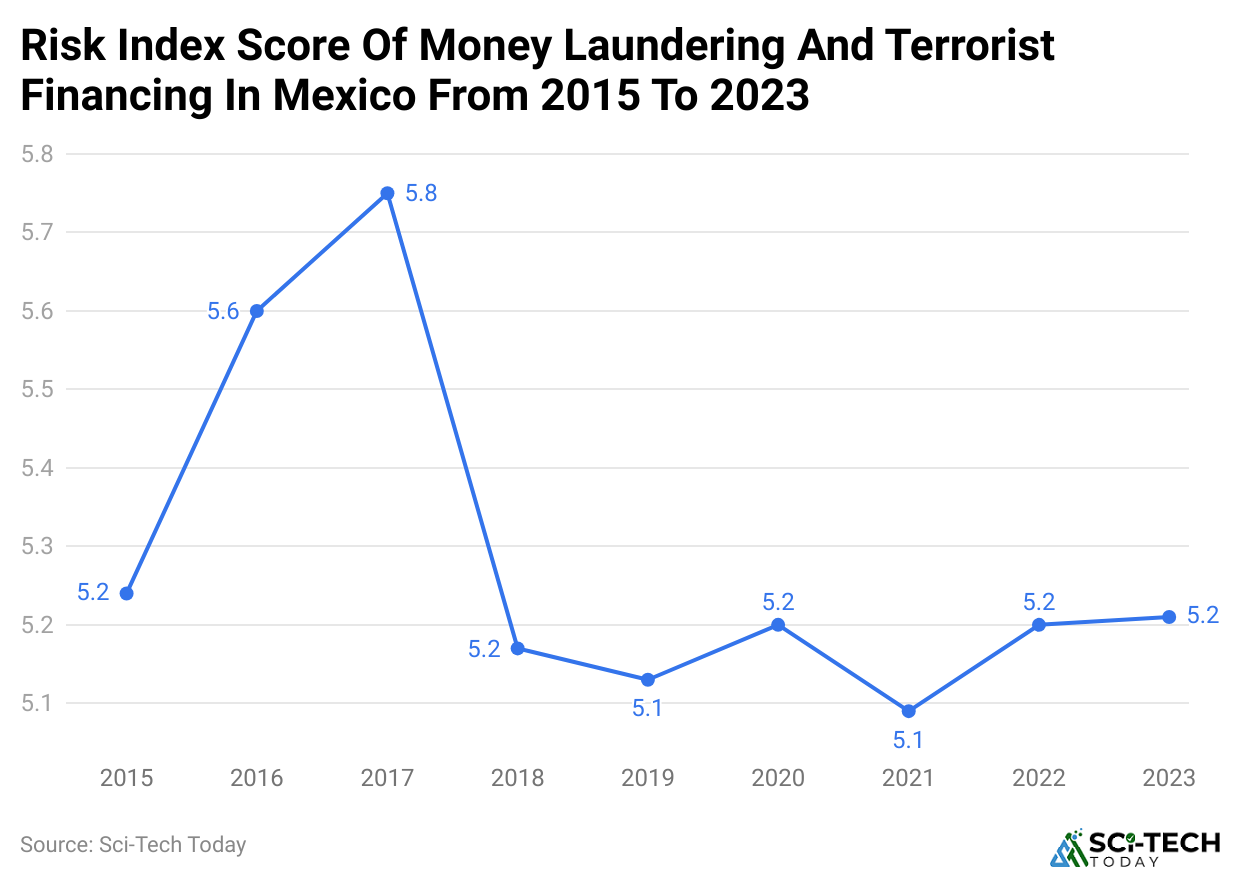
- According to money laundering statistics, The money laundering financing risk index for Mexico reached a value of 5.21 in the year 2023, compared to 5.2 a year earlier, which represents a minor increase.
- This index first achieved its peak in 2017, when it recorded a value of 5.75.
- The Basel AML Index is composed of multiple factors, including 14 layers of factors, including corrupt practices, financial containment, open politics, and law.
- This aims to evaluate the money laundering and counter-terrorist financing risks in various countries.
- The data used to measure this index is already in the public domain from FATF, Transparency International, World Bank, and World Economic Forum, and this is used for further analysis.
Reports of Suspected Money Laundering By the Reporting Group
 (Reference: statista.com)
(Reference: statista.com)
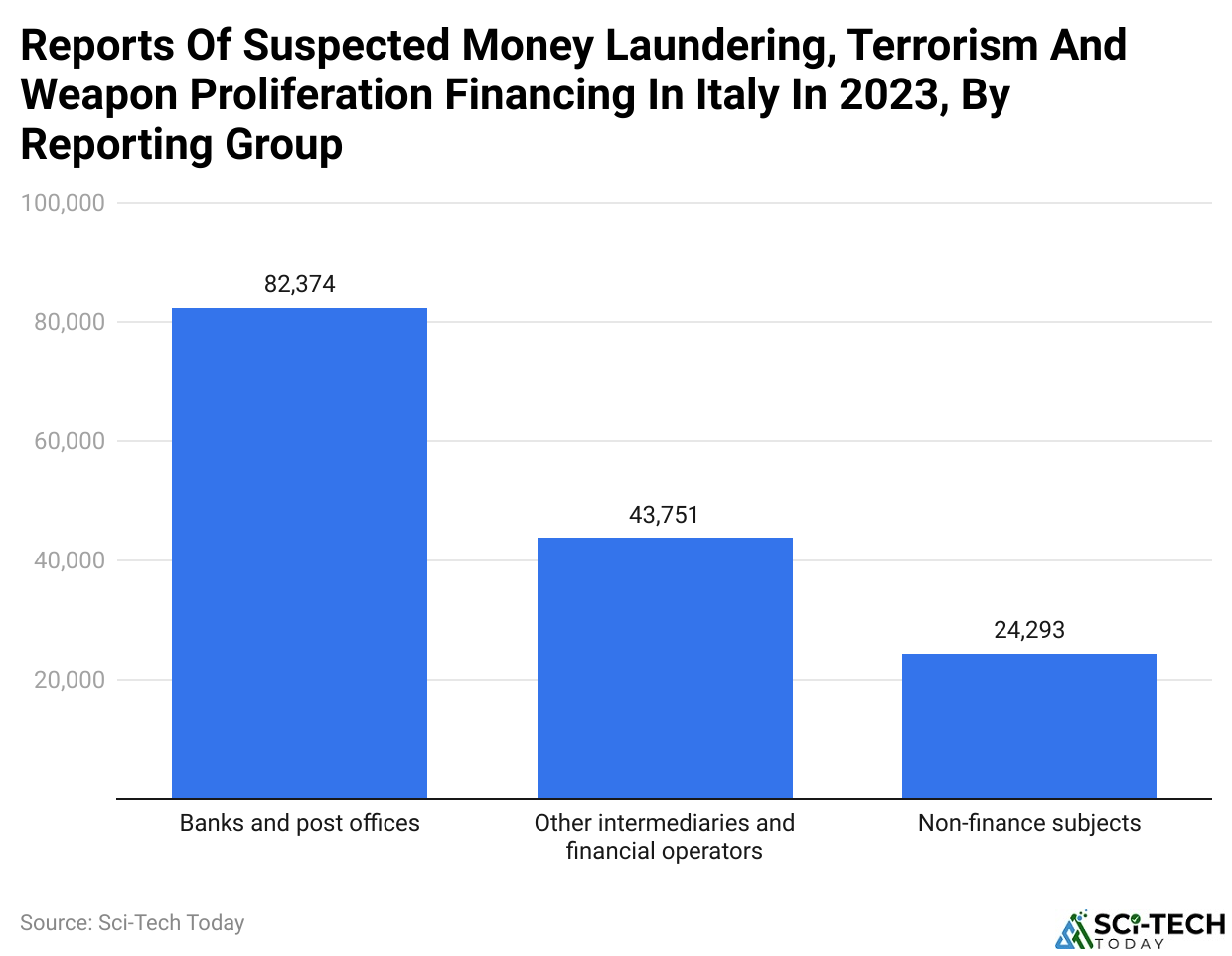
- Money laundering statistics reveal that during the year 2023, the Italian authorities registered 150,418 suspicious transactions or activities.
- Most of these activities came from banks and post offices. They revolved around requests linked to suspicion of money laundering, self-reporting, terrorist financing, and weapons of mass destruction proliferation activities.
Money Laundering By Country
United States
- As a significant economy globally and a well-known financial center, the United States encounters serious problems in overcoming money laundering.
- It is said that banks and other financial institutions in the USA are used every year to launder billions of dollars.
- The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) is the chief agency in the fight against money laundering and ensures compliance with many anti-money laundering (AML) measures.
- An estimated 5 trillion dollars is laundered every year across the world; fiat currencies account for 400 times more for this amount than cryptocurrencies.
- Thus, FinCEN imposes a reportable amount of $300,000 for any suspicious transaction report; however, 95% of the warning bells ringing from its system turn out to be non-threatening events.
United Kingdom
- In the UK, for instance, 30% of money mules are aged below 21, with London remaining a money laundering center for ages.
- The National Crime Agency (NCA) estimates that hundreds of billions of pounds are laundered in this country every year.
- Therefore, measures such as the introduction of the Fifth Money Laundering Directive and the establishment of the Office for Professional Body Anti-Money Laundering Supervision (OPBAS) have been employed in the efforts against money laundering.
Russia
- In Russia, money laundering allegations are mostly associated with corruption, organized crime, and the movement of money outside a country through illegitimate channels.
- A study by Global Financial Integrity (GFI) found that Russia recorded in-situ outflows of illegal trade to the tune of approximately $97.4 million in recent years, when the bulk of the traced economy was supported by proprietary and unrealized estimates.
China
- Given its meteoric rise in the economic sphere, accompanied by very high levels of corruption, China is yet another country that is attractive to money laundering.
- While China has implemented measures to combat this, including the establishment of the China Anti-Money Laundering Monitoring and Analysis Center (CAMLMAC) and stringent laws on AML, billions of dollars in illicit outflows continue to pose a problem.
Mexico
- Concerning drug trafficking, Mexico is both a key transit country and a destination country. Therefore, money laundering is a component that has always existed.
- Illegal property is concealed in practice by organized crime in many ways, such as through forms of laundering like trade-based laundering or structuring.
- Regardless, Mexico has already put more effort into its anti-money laundering regime and is working together with foreign partners.
Switzerland
- On the other hand, while the country was perceived as a global ‘financial paradise’ in the period before 2008, when the world financial crisis broke out, after that and even since this decade for years, it has worked hard in the direction of transparency and restraining the illicit capital movement.
- Nevertheless, according to the assessment carried out by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), there is still room for improvement in the Swiss legal framework as well as in law enforcement practice.
Offshore Financial Centers
- Tens of the clients from such countries as the Caymans, BVI, and Panama, well-known for money laundering and offering offshore services, have also been common targets of money laundering, given their beneficial tax regimes and stringent confidentiality laws, often acting as the last layer to conceal the origin of dirty money.
Issues and Cases Of Money Laundering
- Due to its intricacy and global nature, money laundering is considered to be one of the biggest threats to governments, law and order agencies, and financial systems.
- According to money laundering statistics, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime insists that around 80 billion to over two trillion dollars, equivalent to 2-5% of the world’s GDP, is laundered every year.
- Corruption is a prime factor, with the World Bank estimating annual global losses of over 1.5 trillion dollars because of corruption, which allows money laundering.
- Money-making criminal operations that engage in smuggling, human trafficking, and drug trafficking, among other activities, also involve complex financial networks to conceal the proceeds of their criminal enterprises.
- Additionally, new technologies such as cryptocurrencies and virtual currencies have easy ways of laundering dirty money.
- Anonymity and minimal supervision offered by peer-to-peer systems and decentralized cryptocurrencies are especially enhancements for money launderers.
- Still, according to the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), a lot of the new developing nations have challenges in their anti-money laundering measures, carrying factors that definitely can be addressed.
- Money laundering is not only an economic issue. It encourages crime, increases poverty levels, destroys the population’s faith in the financial system, and causes many other kinds of social damage.
Conclusion
The rise in monetary crime has a far-reaching effect on the world in general, and money laundering statistics in 2024 are no different as it account for billions of dollars lost annually. The use of currencies that can be manipulated easily, along with advanced methods of trade-based crimes, makes it practically impossible to chase and apprehend offenders.
However, with the advent of advanced technologies and strict laws, the global community is pushing hard against this menace. There is no automatic win in the fight against money laundering, especially with the criminals who will always reinvent themselves.
FAQ.
Laundering and integration of illicit money into the legal economy remain a major global issue even in the year 2024, with estimates suggesting that between 800 billion dollars to 2 trillion dollars is laundered in a given financial year, which is about 2-5% of total global GDP.
The techniques for laundering money include offshore accounts, shell corporations, real estate, and, most speaking, the year 2024 – cryptocurrencies. Crimes committed using cryptos are rather impressive figures as a total of 23 billion us dollars have been laundered through cryptos, up by 30% of 2023.
In 2024, it is estimated that 35% of global money laundering activities will occur in North America, largely in the USA, followed by Europe at 25%, mainly due to countries in Eastern Europe and the offshore centres. The Asia Pacific region, including China and India, will account for 22% of the total due to the growing trend of cryptocurrency usage in this region.
In 2024, banks and other financial organisations account for approximately 70% of all money laundering activities within the global economy. Even with the implementation of regulations, many of the companies find it difficult to eliminate the money laundering practices.
One of the primary threats to the effectiveness of laws aimed at combating money laundering is the growing popularity of virtual currencies, the increased use of identity-cloak technologies and the expansion of global financial systems. Countries with weak or ineffective governments, such as corrupt countries or countries with weak anti-money laundering measures, are still in trouble, and that is why it is transnational.

Barry is a technology enthusiast with a passion for in-depth research on various technological topics. He meticulously gathers comprehensive statistics and facts to assist users. Barry's primary interest lies in understanding the intricacies of software and creating content that highlights its value. When not evaluating applications or programs, Barry enjoys experimenting with new healthy recipes, practicing yoga, meditating, or taking nature walks with his child.